
The copy we are selling is similar to the one pictured above.
Sonic Grade
Side One: 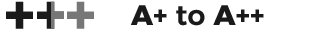
Side Two: 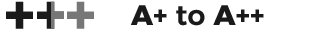
Vinyl Grade
Side One: Mint Minus Minus
Side Two: Mint Minus Minus (closer to M-- to EX++ in parts)*
- This vintage White Dog pressing of Reiner and the Chicago Symphony's performance of this dazzling symphonic suite boasts very good Hot Stamper Living Stereo sound from first note to last
- We guarantee there is more richness, fullness, and performance energy on this copy than others you've heard, and that's especially true if you own any of the Heavy Vinyl pressings that are currently on the market
- Our favorite Scheherazade for about the last 15 years or so has been the one Ansermet conducted for Decca in 1961, but the roller-coaster excitement Reiner and the CSO bring to the fourth movement is something very special
- True, the side with the fourth movement earned a minimal Hot Stamper grade of 1.5+, but we still guarantee that it will beat the pants off any Heavy Vinyl reissue, because every one of those that we played was ridiculously opaque, muddy and thick enough to have us crying "uncle" after five minutes (reviews available on the blog)
- Marks in the vinyl are sometimes the nature of the beast with these early pressings - there simply is no way around them if the superior sound of vintage analog is important to you
More of the music of Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov (1844-1908) / More Living Stereo Recordings

100% Money Back Guarantee on all Hot Stampers
FREE Domestic Shipping on all LP orders over $150
*NOTE: There is a mark that plays 16 times lightly approx. 30 seconds into the first track / third movement on side 2, "The Young Prince and the Young Princess."
*NOTE: Side two of this record was not noisy enough to rate our M-- to EX++ grade, but it's not quite up to our standards for Mint Minus Minus either. If you're looking for quiet vinyl, this is probably not the best copy for you.
We did a monster shootout for this music in 2014, one we had been planning for more than two years. On hand were quite a few copies of the Reiner on RCA; the Ansermet on London (CS 6212, his second stereo recording, from 1961, not the earlier and noticeably poorer sounding recording from in 1959); the Ormandy on Columbia, and a few others we felt had potential.
The only recordings that held up all the way through -- the fourth movement being the Ball Breaker of all time, for both the engineers and musicians -- were those by Reiner and Ansermet. This was disappointing considering how much time and money we spent finding, cleaning and playing those ten or so other pressings, but such is the nature of our business.
This vintage Living Stereo pressing has the kind of Tubey Magical Midrange that modern records can barely BEGIN to reproduce. Folks, that sound is gone and it sure isn't showing signs of coming back. If you love hearing INTO a recording, actually being able to "see" the performers, and feeling as if you are sitting in the studio with the band, this is the record for you. It's what vintage all analog recordings are known for -- this sound.
If you exclusively play modern repressings of vintage recordings, I can say without fear of contradiction that you have never heard this kind of sound on vinyl. Old records have it -- not often, and certainly not always -- but maybe one out of a hundred new records do, and those are some pretty long odds.
What The Best Sides Of Scheherazade Have To Offer Is Not Hard To Hear
- The biggest, most immediate staging in the largest acoustic space
- The most Tubey Magic, without which you have almost nothing. CDs give you clean and clear. Only the best vintage vinyl pressings offer the kind of Tubey Magic that was on the tapes in 1960
- Tight, note-like, rich, full-bodied bass, with the correct amount of weight down low
- Natural tonality in the midrange -- with all the instruments having the correct timbre
- Transparency and resolution, critical to hearing into the three-dimensional studio space
No doubt there's more but we hope that should do for now. Playing the record is the only way to hear all of the qualities we discuss above, and playing the best pressings against a pile of other copies under rigorously controlled conditions is the only way to find a pressing that sounds as good as this one does.
Copies with rich lower mids and nice extension up top did the best in our shootout, assuming they weren't veiled or smeary of course. So many things can go wrong on a record! We know, we've heard them all.
Top end extension is critical to the sound of the best copies. Lots of old records (and new ones) have no real top end; consequently, the studio or stage will be missing much of its natural air and space, and instruments will lack their full complement of harmonic information.
Tube smear is common to most vintage pressings. The copies that tend to do the best in a shootout will have the least (or none), yet are full-bodied, tubey and rich.
Standard Operating Procedures
What are sonic qualities by which a record -- any record -- should be judged? Pretty much the ones we discuss in most of our Hot Stamper listings: energy, frequency extension (on both ends), transparency, spaciousness, harmonic textures (freedom from smear is key), rhythmic drive, tonal correctness, fullness, richness, three-dimensionality, and on and on down the list.
When we can get a number of these qualities to come together on the side we’re playing, we provisionally give it a ballpark Hot Stamper grade, a grade that is often revised during the shootout as we hear what the other copies are doing, both good and bad.
Once we’ve been through all the side ones, we play the best of the best against each other and arrive at a winner for that side. Other copies from earlier in the shootout will frequently have their grades raised or lowered based on how they sounded compared to the eventual shootout winner. If we’re not sure about any pressing, perhaps because we played it early on in the shootout before we had learned what to listen for, we take the time to play it again.
Repeat the process for side two and the shootout is officially over. All that’s left is to see how the sides of each pressing match up.
It may not be rocket science, but it’s a science of a kind, one with strict protocols that we’ve developed over the course of many years to insure that the results we arrive at are as accurate as we can make them.
The result of all our work speaks for itself, on this very record in fact. We guarantee you have never heard this music sound better than it does on our Hot Stamper pressing -- or your money back.
What We're Listening For On Scheherazade
- Energy for starters. What could be more important than the life of the music?
- The Big Sound comes next -- wall to wall, lots of depth, huge space, three-dimensionality, all that sort of thing.
- Then transient information -- fast, clear, sharp attacks, not the smear and thickness so common to these LPs.
- Powerful bass -- which ties in with good transient information, also the issue of frequency extension further down.
- Next: transparency -- the quality that allows you to hear deep into the soundfield, showing you the space and air around all the instruments.
- Extend the top and bottom and voila, you have The Real Thing -- an honest to goodness Hot Stamper.
TAS List
Harry Pearson put this record on his TAS list of super discs.
Of course, the fact that a recording is on the TAS list doesn’t guarantee that the pressing you buy will have great sound, but Better Records does precisely that. If you don’t think a record sounds as good as we’ve described it, we’ll always happily take that record back and refund your money.
Vinyl Condition
Mint Minus Minus and maybe a bit better is about as quiet as any vintage pressing will play, and since only the right vintage pressings have any hope of sounding good on this album, that will most often be the playing condition of the copies we sell. (The copies that are even a bit noisier get listed on the site are seriously reduced prices or traded back in to the local record stores we shop at.)
Those of you looking for quiet vinyl will have to settle for the sound of other pressings and Heavy Vinyl reissues, purchased elsewhere of course as we have no interest in selling records that don't have the vintage analog magic of these wonderful recordings.
If you want to make the trade-off between bad sound and quiet surfaces with whatever Heavy Vinyl pressing might be available, well, that's certainly your prerogative, but we can't imagine losing what's good about this music -- the size, the energy, the presence, the clarity, the weight -- just to hear it with less background noise.
Side One
- The Sea and Sinbad’s Ship
- The Story of the Kalendar Prince
Side Two
- The Young Prince and the Young Princess
- Festival in Bagdad; The Sea; The Ship Goes to Pieces on a Rock Surmounted by a Bronze Warrior
Wikipedia on Scheherazade
Scheherazade, also commonly Sheherazade, Op. 35, is a symphonic suite composed by Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov in 1888 and based on One Thousand and One Nights (also known as The Arabian Nights).
This orchestral work combines two features typical of Russian music in general and of Rimsky-Korsakov in particular: dazzling, colorful orchestration and an interest in the East, which figured greatly in the history of Imperial Russia, as well as orientalism in general. The name "Scheherazade" refers to the main character Scheherazade of the One Thousand and One Nights. It is one of Rimsky-Korsakov's most popular works.
During the winter of 1887, as he worked to complete Alexander Borodin's unfinished opera Prince Igor, Rimsky-Korsakov decided to compose an orchestral piece based on pictures from One Thousand and One Nights as well as separate and unconnected episodes. After formulating musical sketches of his proposed work, he moved with his family to the Glinki-Mavriny dacha, in Nyezhgovitsy along the Cherementets Lake (near present-day Luga, in Leningrad Oblast). The dacha where he stayed was destroyed by the Germans during World War II.
During the summer, he finished Scheherazade and the Russian Easter Festival Overture. Notes in his autograph orchestral score show that the former was completed between June 4 and August 7, 1888. Scheherazade consisted of a symphonic suite of four related movements that form a unified theme. It was written to produce a sensation of fantasy narratives from the Orient.
Initially, Rimsky-Korsakov intended to name the respective movements in Scheherazade "Prelude, Ballade, Adagio and Finale." However, after weighing the opinions of Anatoly Lyadov and others, as well as his own aversion to a too-definitive program, he settled upon thematic headings, based upon the tales from The Arabian Nights.
The composer deliberately made the titles vague so that they are not associated with specific tales or voyages of Sinbad. However, in the epigraph to the finale, he does make reference to the adventure of Prince Ajib. In a later edition, Rimsky-Korsakov did away with titles altogether, desiring instead that the listener should hear his work only as an Oriental-themed symphonic music that evokes a sense of the fairy-tale adventure, stating:
"All I desired was that the hearer, if he liked my piece as symphonic music, should carry away the impression that it is beyond a doubt an Oriental narrative of some numerous and varied fairy-tale wonders and not merely four pieces played one after the other and composed on the basis of themes common to all the four movements."
He went on to say that he kept the name Scheherazade because it brought to everyone’s mind the fairy-tale wonders of Arabian Nights and the East in general.
Musical Overview
Rimsky-Korsakov wrote a brief introduction that he intended for use with the score as well as the program for the premiere:
"The Sultan Schariar, convinced that all women are false and faithless, vowed to put to death each of his wives after the first nuptial night. But the Sultana Scheherazade saved her life by entertaining her lord with fascinating tales, told seriatim, for a thousand and one nights. The Sultan, consumed with curiosity, postponed from day to day the execution of his wife, and finally repudiated his bloody vow entirely."
The grim bass motif that opens the first movement represents the domineering Sultan.
This theme emphasizes four notes of a descending whole tone scale: E–D–C–B♭ (each note is a down beat, i.e. first note in each measure, with A♯ for B♭). After a few chords in the woodwinds, reminiscent of the opening of Mendelssohn's A Midsummer Night's Dream overture, the audience hears the leitmotif that represents the character of the storyteller herself, Scheherazade. This theme is a tender, sensuous, winding melody for violin solo, accompanied by harp.
Rimsky-Korsakov stated:
"The unison phrase, as though depicting Scheherazade’s stern spouse, at the beginning of the suite appears as a datum, in the Kalendar’s Narrative, where there cannot, however, be any mention of Sultan Shakhriar. In this manner, developing quite freely the musical data taken as a basis of composition, I had to view the creation of an orchestral suite in four movements, closely knit by the community of its themes and motives, yet presenting, as it were, a kaleidoscope of fairy-tale images and designs of Oriental character."
Rimsky-Korsakov had a tendency to juxtapose keys a major third apart, which can be seen in the strong relationship between E and C major in the first movement. This, along with his distinctive orchestration of melodies which are easily comprehensible, assembled rhythms, and talent for soloistic writing, allowed for such a piece as Scheherazade to be written.
The movements are unified by the short introductions in the first, second and fourth movements, as well as an intermezzo in the third. The last is a violin solo representing Scheherazade, and a similar artistic theme is represented in the conclusion of the fourth movement. Writers have suggested that Rimsky-Korsakov's earlier career as a naval officer may have been responsible for beginning and ending the suite with themes of the sea. The peaceful coda at the end of the final movement is representative of Scheherazade finally winning over the heart of the Sultan, allowing her to at last gain a peaceful night's sleep.
The music premiered in Saint Petersburg on October 28, 1888, conducted by Rimsky-Korsakov.
The reasons for its popularity are clear enough; it is a score replete with beguiling orchestral colors, fresh and piquant melodies, a mild oriental flavor, a rhythmic vitality largely absent from many major orchestral works of the later 19th century, and a directness of expression unhampered by quasi-symphonic complexities of texture and structure.
Movements
The Sea and Sinbad's Ship
This movement is made up of various melodies and contains a general A B C A′ B C′ form. Although each section is highly distinctive, aspects of melodic figures carry through and unite them into a movement. Although similar in form to the classical symphony, the movement is more similar to the variety of motives used in one of Rimsky-Korsakov's previous works, Antar. Antar, however, used genuine Arabic melodies as opposed to Rimsky-Korsakov’s own ideas of an oriental flavor.
The Story of the Kalendar Prince
This movement follows a type of ternary theme and variation and is described as a fantastic narrative. The variations only change by virtue of the accompaniment, highlighting the piece's "Rimsky-ness" in the sense of simple musical lines allowing for greater appreciation of the orchestral clarity and brightness. Inside the general melodic line, a fast section highlights changes of tonality and structure.
The Young Prince and the Young Princess
This movement is also ternary and is considered the simplest movement in form and melodic content. The inner section is said to be based on the theme from Tamara, while the outer sections have song-like melodic content. The outer themes are related to the inner by tempo and common motif, and the whole movement is finished by a quick coda return to the inner motif, balancing it out nicely.
Festival at Baghdad. The Sea. The Ship Breaks against a Cliff Surmounted by a Bronze Horseman
This movement ties in aspects of all the preceding movements as well as adding some new ideas, including an introduction of both the beginning of the movement and the Vivace section based on Sultan Shakhriar’s theme, a repeat of the main Scheherazade violin theme, and a reiteration of the fanfare motif to portray the ship wreck. Coherence is maintained by the ordered repetition of melodies, and continues the impression of a symphonic suite, rather than separate movements. A final conflicting relationship of the subdominant minor Schahriar theme to the tonic major cadence of the Scheherazade theme resolves in a fantastic, lyrical, and finally peaceful conclusion.
